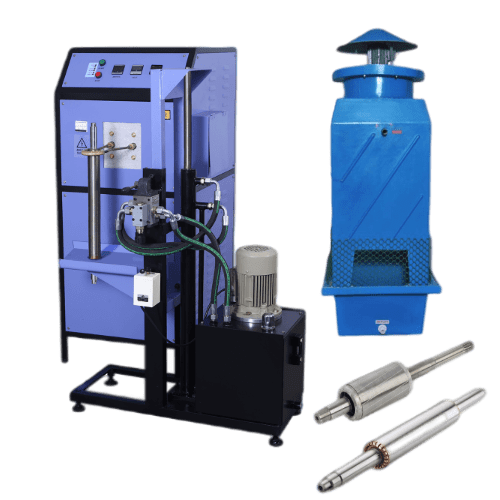
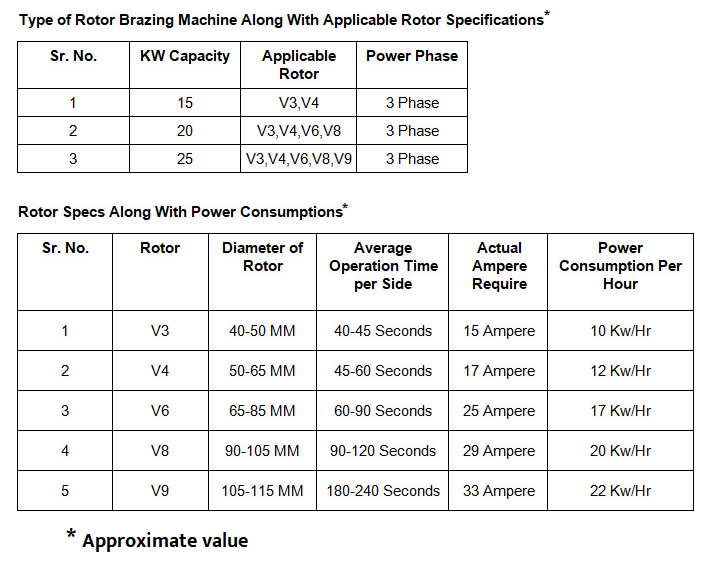
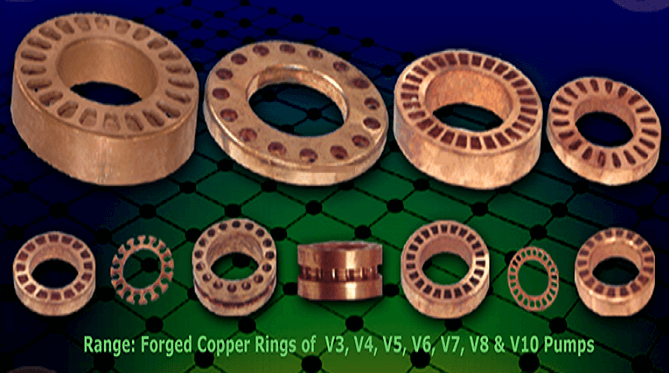
| High efficiency: The mini induction machine features a high efficiency design, allowing for maximum energy conversion and reduced power consumption. |
| Compact size: With its compact size, the mini induction machine is ideal for applications where space is limited. |
| Low noise operation: The machine operates with minimal noise, ensuring a quiet and comfortable working environment. |
| Reliable performance: Built with high-quality components, the mini induction machine offers reliable and consistent performance. |
| Easy installation: The machine is designed for easy installation, making it convenient for users to set up and use. |
| Advanced control features: Equipped with advanced control features, the machine allows for precise and efficient operation. |
| afety features: The machine is equipped with various safety features to ensure safe operation and prevent accidents. |
| Cost-effective: With its high efficiency and reliable performance, the mini induction machine offers a cost-effective solution for various electrical needs. |